Windows x64 ABI quick reference.
Posted on February 16, 2019
Use at your own risk!
If something is unclear here are the official docs.
I think they are pretty well written as far as these things go.
Caller/Calle Saved
Callee Saved - nonvolatile:
RBX, RBP, RDI, RSI, RSP, R12, R13, R14, R15, Xmm6+
Caller Saved - volatile:
RAX, RCX, RDX, R8, R9, R10, R11, Xmm0 - Xmm5
Argument passing
Regular calls
| Arg1 | Arg2 | Arg3 | Arg4 | Arg5+ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integer | RCX | RDX | R8 | R9 | Stack |
| Float | XMM0 | XMM1 | XMM2 | XMM3 | Stack |
First four arguments:
- FP values in xmm
- Other values in gp regs if they fit (directly or by reference)
Var Args
First four arguments.
- Float values are passed in Xmm AND general purpose registers.
- Otherwise just like regular calls.
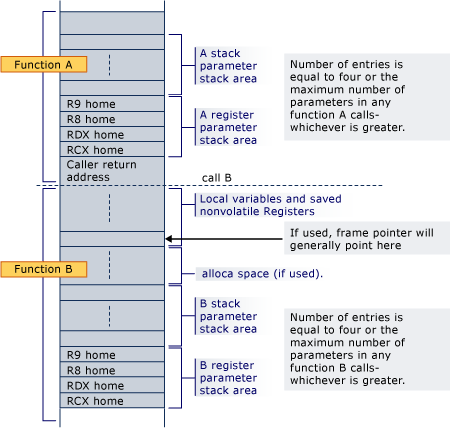
Stack business
- Stack is 16 byte aligned.
- Caller must provide at least space for 4 64bit values on top of actual argument.
This stack space must be considered volatile by the caller.
This can be used to store nonvolatile registers and other things.
Cmm Registers mappings on Amd64:
| Cmm | Assemby |
|---|---|
| HP | R12 |
| SPLim | R15 |
| SP | RBP |
| R1 | RBX |
| R2 | R14 |
| R3 | RSI |
| R4 | RDI |
| R5 | R8 |
| R6 | R9 |